Mass-action ratio
The mass-action ratio[1], often denoted by 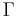 , is the ratio of product concentrations to reactant concentrations.
, is the ratio of product concentrations to reactant concentrations.
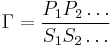
If the product and reactant concentrations are at equilibrium then the mass-action ratio will equal the equilibrium constant. At equilibrium:
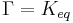
The ratio of the mass-action ratio to the equilibrium constant is often called the disequilibrium ratio, denoted by the symbol 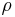 .
.
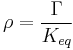
At equilibrium 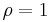 . When the reaction is out of equilibrium
. When the reaction is out of equilibrium 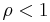 but always greater than zero.
but always greater than zero.
References
- ^ B. Hess and K. Brand. (1965). Enzymes and metabolite profiles. In Control of energy metabolism. III. Ed. B. Chance, R. K. Estabrook and J. R. Williamson. New York: Academic Press.
Other sources
- Atkins, P.W. (1978). Physical Chemistry Oxford University Press ISBN 0-7167-3539-X
- Trevor Palmer (2001) Enzymes: biochemistry, biotechnology and clinical chemistry Chichester Horwood Publishing ISBN 1-8985-6378-0